In modern manufacturing companies, a high degree of automation and sensitive electronic equipment make power supply stability a critical factor. One of the biggest threats – overvoltages – can cause costly damage, production downtime, and significant losses.
An overvoltage is a sudden and short-term increase in electrical voltage in the network that can seriously damage or completely destroy electronic devices. It can occur in various ways – from lightning strikes to power supply disturbances or switching on large loads in the electrical network.
An overvoltage is a sudden, short-term increase in electrical voltage in the network that can:
Main causes of overvoltage:
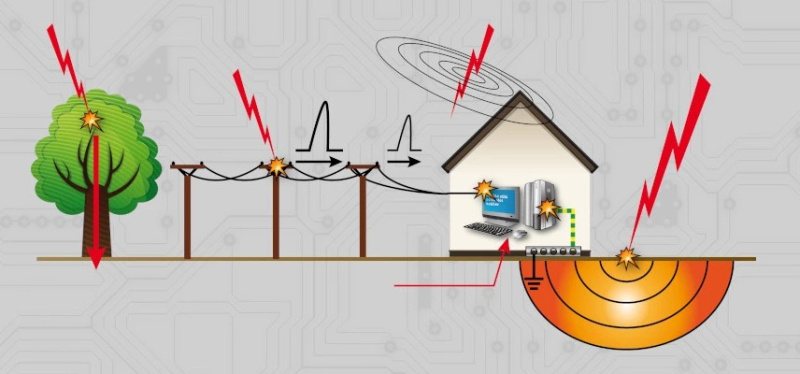
 One of the most dangerous causes of overvoltage is lightning strikes. Even if lightning does not directly strike a building, a nearby discharge or a strike on power lines can cause massive voltage surges in the network, damaging all connected equipment within a fraction of a second. In industrial zones, where there are many metal structures and electrical connections, lightning-induced overvoltages can result in massive losses.
One of the most dangerous causes of overvoltage is lightning strikes. Even if lightning does not directly strike a building, a nearby discharge or a strike on power lines can cause massive voltage surges in the network, damaging all connected equipment within a fraction of a second. In industrial zones, where there are many metal structures and electrical connections, lightning-induced overvoltages can result in massive losses.
Level 2 – Type 2 (T2) – secondary protection. Type 2 devices are the most commonly used protection type, designed to suppress medium-level overvoltages in distribution boards and substations.
Level 3 – Type 3 (T3) – local protection. Positioned closer to sensitive electronic devices (PLCs, HMIs, I/O modules, computers, sensors), which can be damaged even by small voltage spikes.
Combined solutions – Type 2+3 and signal protection
In addition to T1–T3 protection, modern equipment also requires protection for control circuits and data signals (e.g., 0–10V, 4–20 mA, Ethernet/PoE).
SIA “ZTF Lāsma” offers overvoltage protection solutions from well-known brands such as Schneider Electric, Schrack Technik, and Seneca. The table below shows the main product series and codes according to their application.
| Protection class | Installation location | Iimp / Imax (kA) | Protection level Up | Schneider Electric | Schrack Technik | Seneca |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 (T1) | Main intake / LPS-equipped buildings | 25 | ≤ 1.5 kV | PRD1 25r (16332) | Protec PTNC BC 275 – IS211330 | — |
| Type 2 (T2) | Distribution boards 230/400 V TN-S/TT | 40 | ≤ 1.5 kV | iPRD40r 3P+N – A9L40601 | UAS 4P 40 kA – IS010449 | S400HV-2 |
| Type 2 (3+1 / 2+0) | Sub-distribution / TN-C networks | 40 | ≤ 1.5 kV | iPRD40r 1P+N – A9L40501 | Combtec 12.5 kA – IS211230 | — |
| Type 3 (T3) | Local (PLC, HMI) | 2.5 | ≤ 1.0 kV | iPRD8 3P+N – A9L08600 | UAS T3 1+1 – IS010460 | S400LV-1-N |
| Type 2+3 (24 V DC) | Control power 24 V | 10 | ≤ 55 V | — | — | S400LV-DC24 |
| Signals (0–10 V / 4–20 mA) | Analogue / digital I/O lines | 10 | ≤ 55 V (L-L) ≤ 650 V (L-PE) | — | — | S400CL-1 |
| Data (T3) | Ethernet / PoE (RJ-45) | 10 | ≤ 35 V (diff.) / ≤ 500 V (common) | iPRE RJ45 – A9L16441 | LAN Arrester Cat6 – IS212080 | S400NET-1 |
| PV (T2 DC) | Solar panels 600–1000 V DC | 20 | ≤ 3.8 kV | iPRD40r 1000 DC – A9L40281 | PV SPD Class 2 – IS01121101 | — |
By using industrial-grade overvoltage protection solutions, it is possible to build an effective, three-level protection system that safeguards electrical equipment and infrastructure across different risk levels:
This structured protection approach guarantees:
